At deadly Glacier Peak, one last hurdle for new seismometers
Published 1:30 am Monday, January 17, 2022





DARRINGTON — Snohomish County’s Glacier Peak, classified as one of America’s deadliest volcanoes, is a step closer to getting adequate seismometers to detect future eruptions.
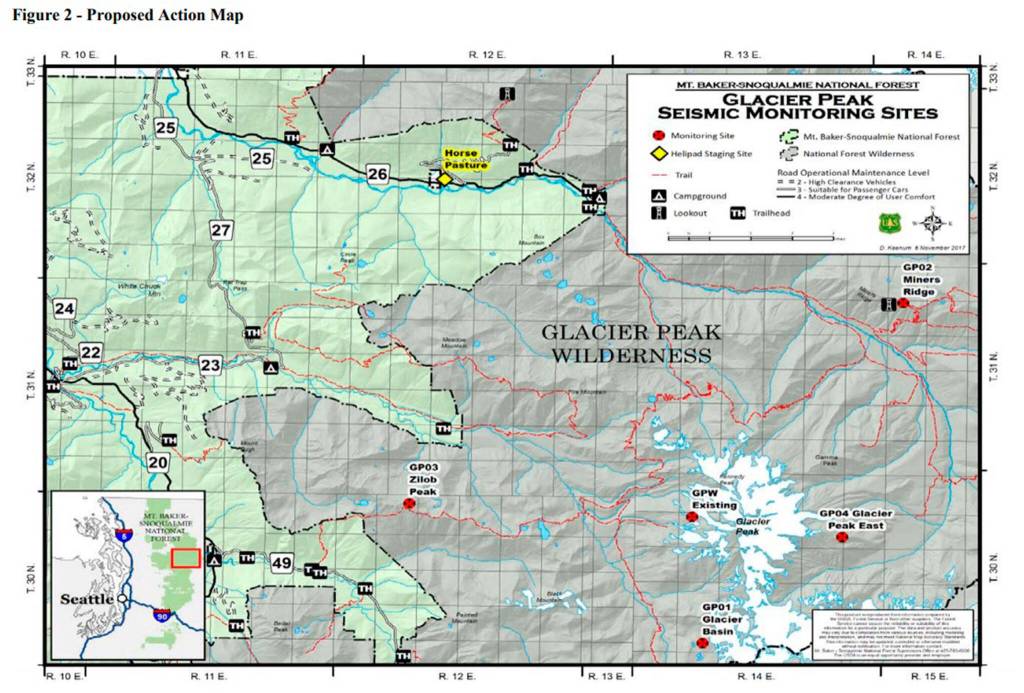
On Friday, the U.S. Forest Service announced it completed an environmental assessment and a draft decision for installing four new monitors and upgrading an old one, as part of a 30-year special use permit. Government officials estimate the GPS stations could detect and locate eight times as many earthquakes.
With a severely lacking early warning system at the volcano, new monitors have been discussed for years. But progress has been paused again and again while agencies worked on other projects, and because of the global pandemic.
Now, new monitors could be installed as soon as this summer, barring further delays, said Forest Service geologist Todd Griffin, who has been managing the project. The equipment could detect geologic changes on the volcano’s surface, increases in gas emissions and earthquakes.
U.S. Geological Survey geophysicist Benjamin Pauk called Glacier Peak one of the agency’s biggest priorities. If everything is approved, he said, his team wouldn’t wait beyond 2023 to install the monitors.
First, the Forest Service has to make it through a 45-day objection period, which started Friday, when legal notice was given in The Daily Herald. If there are objections — Griffin expected at least one — the agency has to address those concerns.
In the past, opposition has primarily come from Wilderness Watch, a Montana-based environmental group that contends the use of helicopters and permanent structures violates the federal Wilderness Act. The Pilchuck Audubon Society also has expressed concerns over impacts to the endangered marbled murrelet and spotted owl.
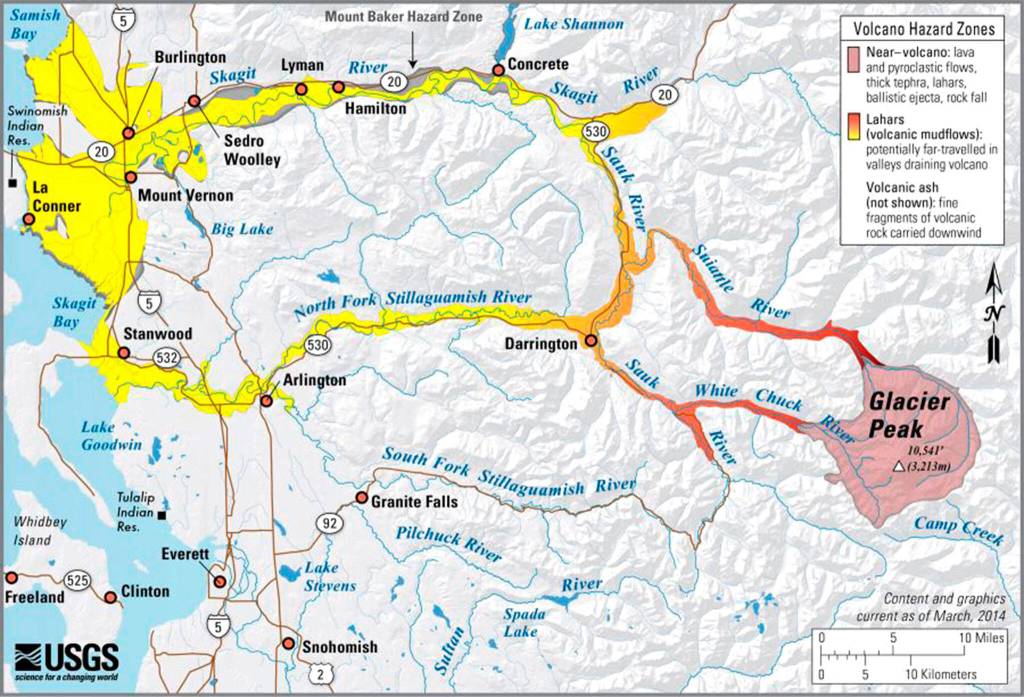
According to a Geological Survey assessment published in 2018, Glacier Peak is the 15th potentially deadliest volcano in the nation, out of 161, based on proximity to communities, previous eruptions and air traffic, among other factors. It was graded as a “very high” threat, along with Mount Rainier, Mount Baker and Mount St. Helens. Mount Adams is considered a “high” threat.
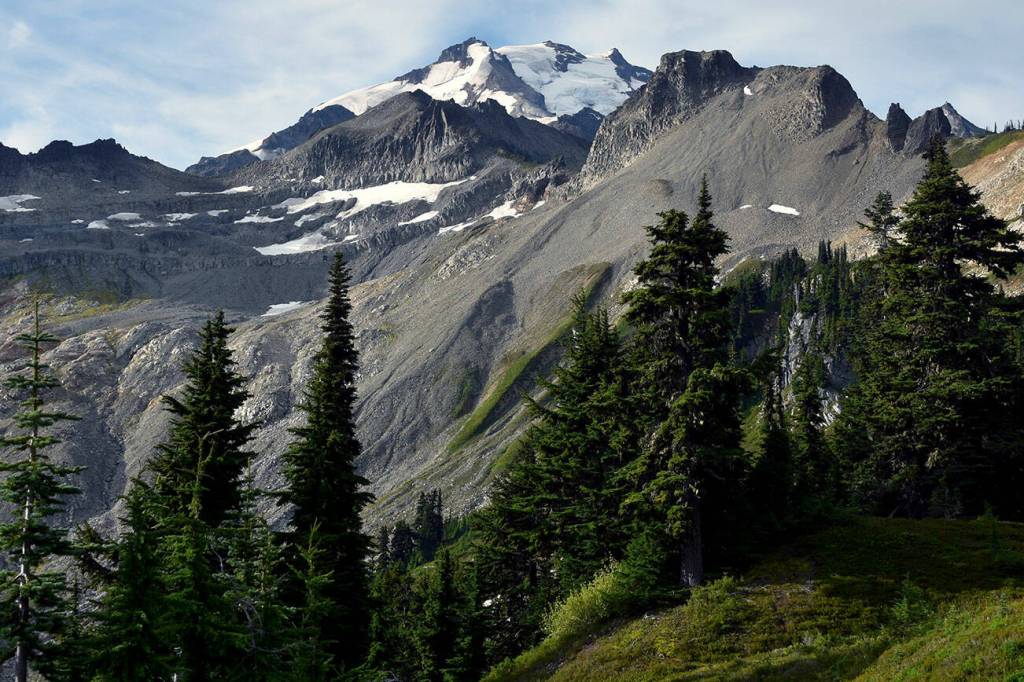
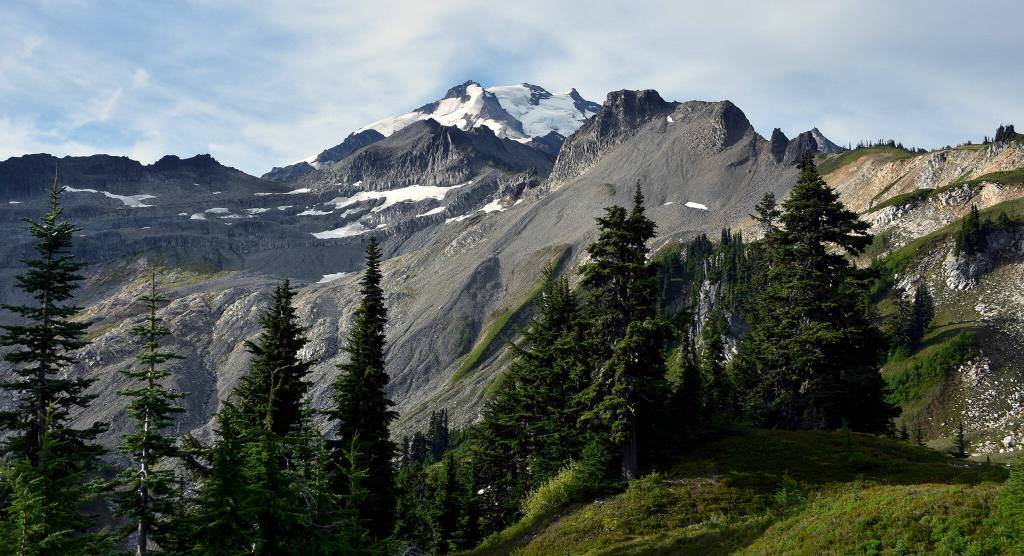
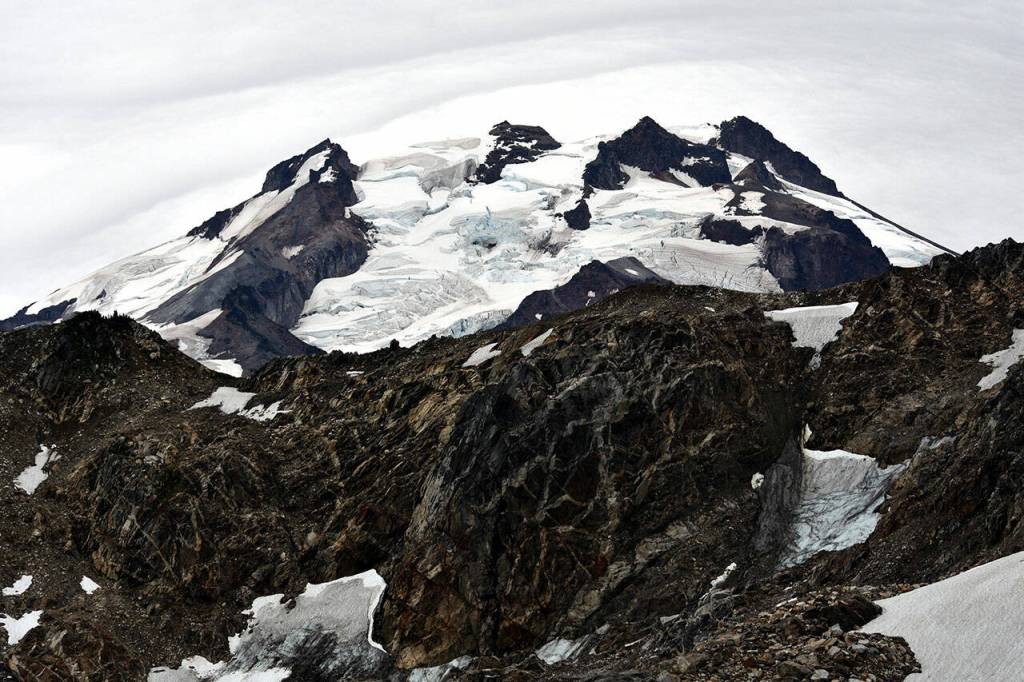
Glacier Peak, at 10,541 feet, is one of the region’s most active volcanoes, according to the Geological Survey. About 13,000 years ago, in one of the largest eruptions in the Cascades since the last Ice Age, the volcano blew off five times as much rock as the 1980 explosion of Mount St. Helens.
In more recent millennia, the volcano has erupted every 500 to 2,000 years or so. The last took place in the 1700s.
Scientists have found evidence of volcanic mudflows, called lahars, along the North Fork Stillaguamish and Skagit rivers, stretching all the way to Puget Sound. Another eruption could wipe out present-day communities like Darrington, a town of about 1,000 people.
According to the Forest Service, 11,000 people visit Glacier Peak Wilderness each year. An average of 930 visitors climb the volcano.
The current analog seismometer transmits data by radio frequency. “It works fine,” Pauk said, “but it’s limited in its ability to detect smaller quakes at deeper depths.”
The way things are now, federal agencies warn catastrophe is possible.
“If adequate systems are not in place and Glacier Peak were to wake up quickly, it is possible that warning signs of an impending eruption could be missed, putting the lives of wilderness users and others in danger,” a Forest Service report says.
The new stations would have a seismometer to measure ground movement, 10 batteries in a fiberglass enclosure with solar panels, and antennae for GPS and data transfer, according to a report from the Forest Service.
The equipment can detect smaller quakes and spot subtle deformations in the earth caused by magma flowing underneath, Pauk said.
And the more stations there are, “the better able we are to identify an earthquake,” he said, as well as whether the earthquake is volcanic in origin.
Each monitor would take about three days and five helicopter trips to install. A helicopter may be needed again every three or five years to replace the heavy batteries.
Crews will not be transported by helicopter. They’ll backpack in to install and maintain the monitors, cutting down on flight time through the wilderness area.
The Forest Service has acknowledged that placing man-made structures and using helicopters would negatively affect the wilderness. However, to be effective, the monitors have to be within a few miles of the summit.
Placing them outside the Glacier Peak Wilderness area was not an option, Griffin said.
In planning the project, he said, the Forest Service balanced the need for more seismometers with the Forest Service’s obligation to protect the wilderness. But it would essentially be impossible to place the monitors without a helicopter, the environmental assessment concluded.
Glacier Peak is uniquely remote. Pauk, a self-professed “average hiker,” said it took him more than two days to reach some of the locations. Many of the trails there are overgrown, he said, and three of the sites don’t have trails leading to them.
The equipment for each site totals 1,900 pounds. Each battery weighs about 70 pounds.
“Trying to backpack those things in basically cross-country just isn’t feasible,” Griffin said.
The Forest Service looked at smaller, lighter equipment, “but they would not meet the needs of monitoring the mountain,” Griffin said.
So the Forest Service arrived at what he called a “happy medium.”
Kevin Proescholdt, conservation director of Wilderness Watch, said staff were still reviewing the environmental assessment and that the organization had not made a decision whether to submit a formal objection. He remained concerned that helicopters and the new permanent structures would disrupt and damage the wilderness area, in violation of the Wilderness Act.
Simply reducing the flight time is not enough, Proescholdt said.
Zachariah Bryan: 425-339-3431; zbryan@heraldnet.com. Twitter: @zachariahtb.
Objection period
Objections are due by Feb. 28. They may be submitted online at cara.ecosystem-management.org/Public//CommentInput?Project=46957.