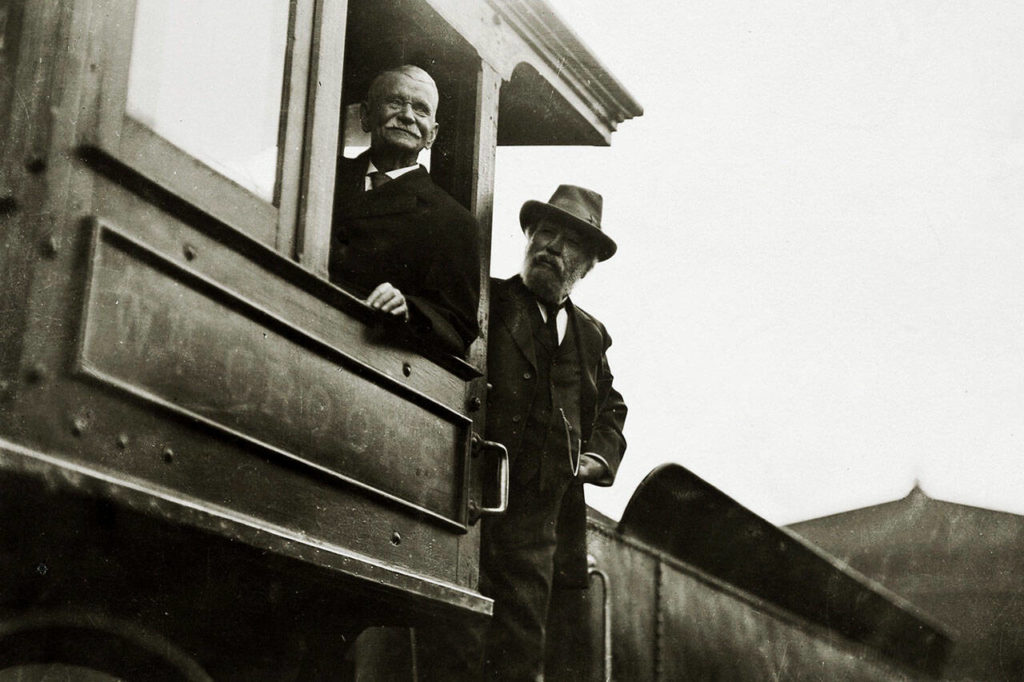
EVERETT — He is one of the most influential American entrepreneurs you’ve probably never heard of.
James J. Hill’s transcontinental railroad spanned from Minnesota to the Pacific Ocean, spurring the success of Washington’s timber, mining and agriculture industries. His vision turned Everett into the “Pittsburgh of the West.”
Hill left an indelible mark on the American economy with the Great Northern Railway. But unlike most of the moguls of the early 20th century, Hill lived in a small Midwest community and excluded his name from his business ventures. He has since faded from modern memory.
Now, two Northwest filmmakers hope to resurrect Hill’s story with their new, four-part documentary series, “The Empire Builder: James J. Hill and the Great Northern Railway.” Released last month, the series by Stephen Sadis and Kyle Kegley explores Hill’s work on the railroad and how it overlapped with labor unions, natural resources, industry, western settlement, immigration, the displacement of Native Americans and wartime finance.
“Here is a man who had relationships with seven different presidents, the first prime minister of Canada and the King of Belgium,” Sadis said. “He was an individual who should be as well known and lauded as J.P. Morgan, Andrew Carnegie and John D. Rockefeller. … It’s a story I think deserves to be told.”
‘An American story’
The Great Northern Railroad’s roots grew out of a local track out of Minnesota that had gone bankrupt three times. In 1878, Hill bought the St. Paul Minneapolis and Manitoba. Eight years later, he started expanding track west.
His plan was to build the shortest transcontinental railroad with a terminus in Puget Sound, so he could offer the cheapest option to transport freight. That meant finding new routes through the Rocky Mountains and the Cascade Range.
Hill enlisted John F. Stevens as his chief surveyor, and Stevens charted both the Marias Pass through the Rockies and his namesake Stevens Pass through the Cascades. (Most other Stevens landmarks in Washington were named for territorial governor Isaac Stevens.)
As Hill’s crews laid the rail line, cities popped up along it to house and entertain workers. Without the help of land grants, like railroaders before him had, Hill invested his own money into those communities to keep them going.
“He took on this kind of patriarchal sort of position with the people he settled in the West and helped them to try and increase their crops,” Sadis said.
Sadis added that Hill had “some self-interest” in the towns, because he wanted to get freight on the trains, but he also seemed to want the settlers to succeed.
The rail project drew millions of immigrants from countries including Germany, Scandinavia and Japan. Sadis estimated 6 million to 8 million people came to the United States as a result of the railroad.
“I just think that’s what makes this more of an American story than a Northwest story, or even just a story about a man and a railroad,” he said.
For Kegley, Hill’s contributions are personal. The third-generation Everett resident said his great grandmother moved west from North Dakota by riding the railroad. Kegley also is the descendant of Scandinavian immigrants who moved to North Dakota in the early 1900s “in large part because of the Great Northern Railway,” he said.
“It’s fun to go back and look at your own family history within the context of what we learned about this project,” Kegley said.
‘Re-emergence of Everett’
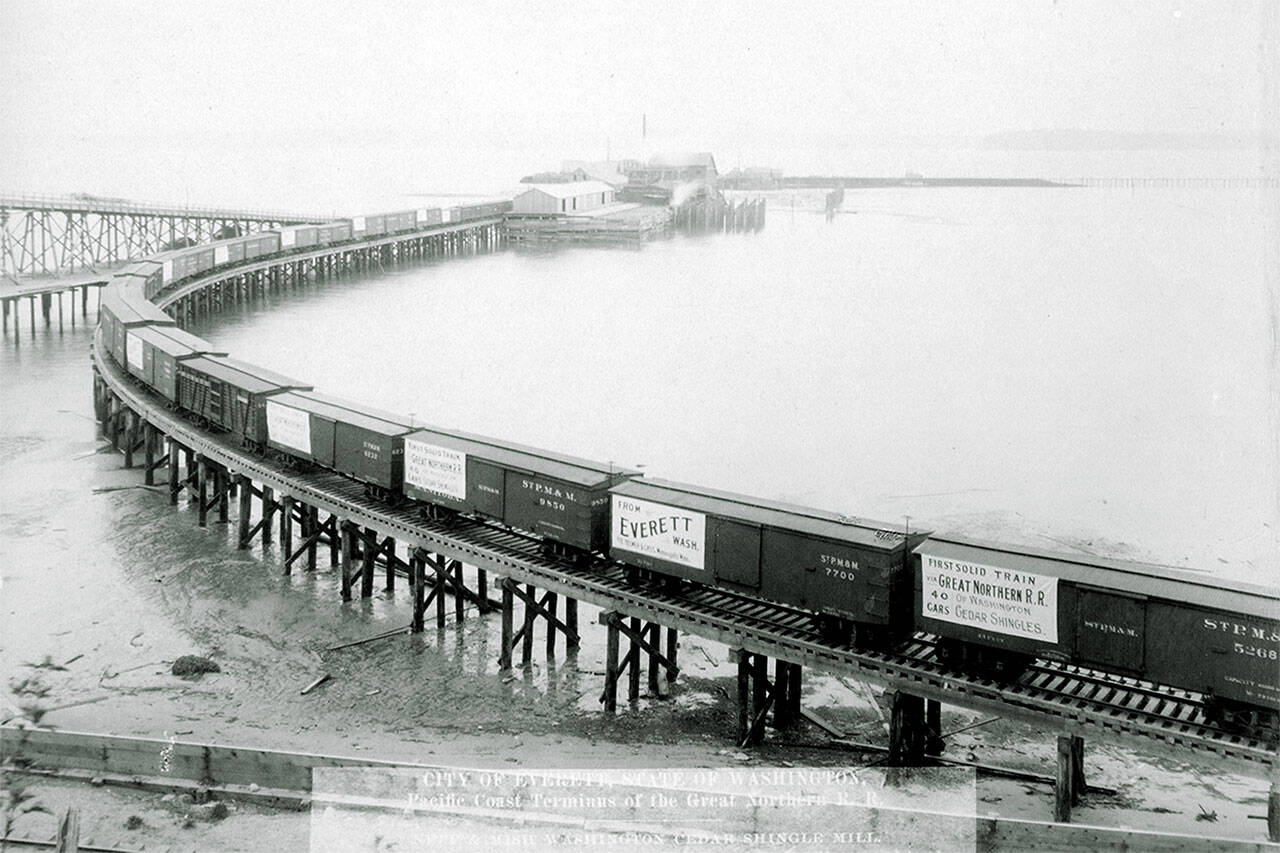
On Jan. 6, 1893, the Great Northern was completed at a length of more than 1,600 miles.
Months later, the economy crashed in what was known as the Panic of 1893. In Everett, the Panic sent investors running. Within two years of the depression, John D. Rockefeller and other investors began selling off their shares to the Everett Land Co.
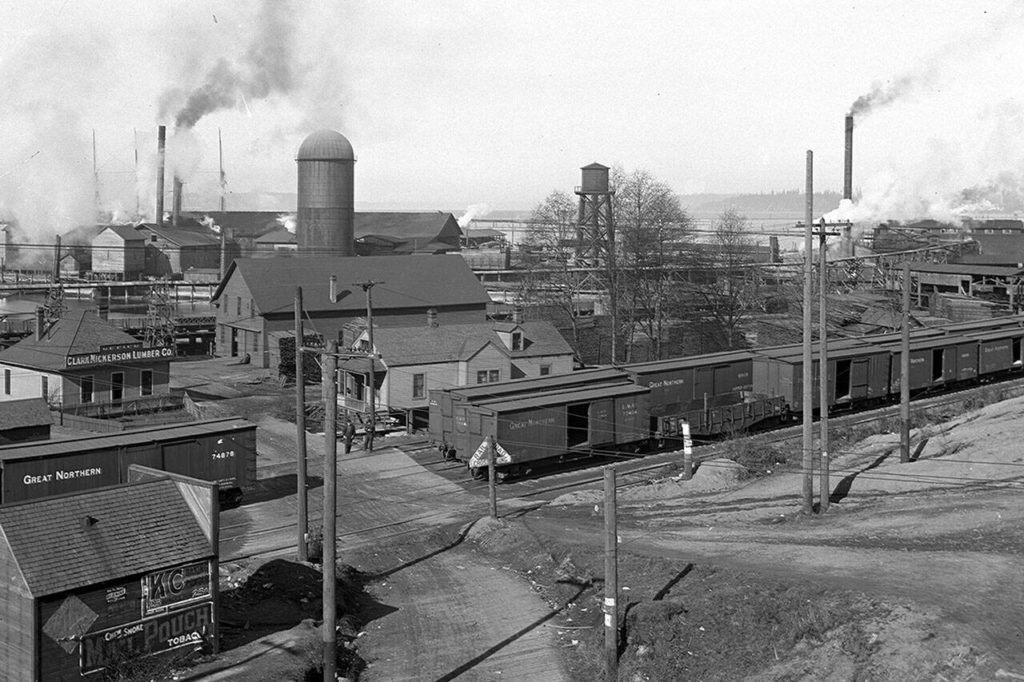
Local factories started to close, wages declined by 60% and the city was nearly bankrupted.
Hill’s railroad was the only line to weather the downturn without declaring bankruptcy. As people pulled out of Everett, Hill purchased their shares and took over. Within a few years, the city rebounded.
From 1900 to 1910, the city tripled in size to 24,000 residents. Everett boasted 10 sawmills and 12 shingle mills, earning its title as the City of Smokestacks. It grew to the third-largest city on Puget Sound.
“It’s really hard to imagine what Everett would have looked like today without James J. Hill,” Kegley said. “After the Panic of 1893, you have people and businesses leaving town in droves, and Hill’s ability to kind of resurrect the town, invest in it personally and bring in new investors is part of the re-emergence of Everett.”
Around the same time as the Panic of 1893, Hill inked what was then the largest private land transaction in American history. He sold 900,000 acres of land to Frederick Weyerhaeuser. The sale fueled the Northwest’s timber industry.
Years later, Hill realized that unregulated logging activity was bound to hurt the environment and the economy. So he began advocating for more sustainable logging, fishing and trade. Hill spoke about the threats of climate change in a speech he gave in 1909, almost seven decades before scientists would formally coin the term.
‘He had no equal’
In Washington, Hill’s “empire” also included Seattle’s King Street Station and Wenatchee’s apple orchards. But his legacy touched many more states, including Montana, Idaho, North Dakota and Minnesota.
Where Carnegie reigned over steel and Rockefeller reigned over oil, Hill ruled timber, iron, copper, agriculture, transportation and finance, Sadis said.
“As one of our interviewees said, he had so many balls in the air, and his legacy is so hard to sum up,” Kegley added. “He had no equal in running his railroad, but he was more than a railroader. … He was kind of a transformative player in this transformative time in American history.”
Hill, though, shied away from fanfare. Instead of a lavish ceremony to celebrate the completion of his railroad, he asked his colleagues to use the money to build a library. He spent his life in his Minnesota home, away from the more glorious New York scene.
“It’s the old situation when you’re in a smaller market, you’re not going to get the national press,” said Sadis, who suggested Hill’s humbleness as one reason his story may have faded.
Kegley and Sadis spent almost 21 years learning about Hill for the docuseries. Sadis said the project started as a one-hour script in 2001 but was shelved twice due to inadequate funding.
In 2017, Sadis and Kegley started Great Northern Filmworks, a nonprofit organization that restarted production of “The Empire Builder.” The script evolved into a four-hour series based on almost 30 interviews and further research, Sadis said.
A two-disc set of “The Empire Builder” is available at greatnorthernfilmworks.com. Viewers can also rent on demand or buy the series on Vimeo.
Mallory Gruben is a Report for America corps member who writes about education for The Daily Herald.
Mallory Gruben: 425-339-3035; mallory.gruben@heraldnet.com; Twitter: @MalloryGruben
Talk to us
> Give us your news tips.
> Send us a letter to the editor.
> More Herald contact information.