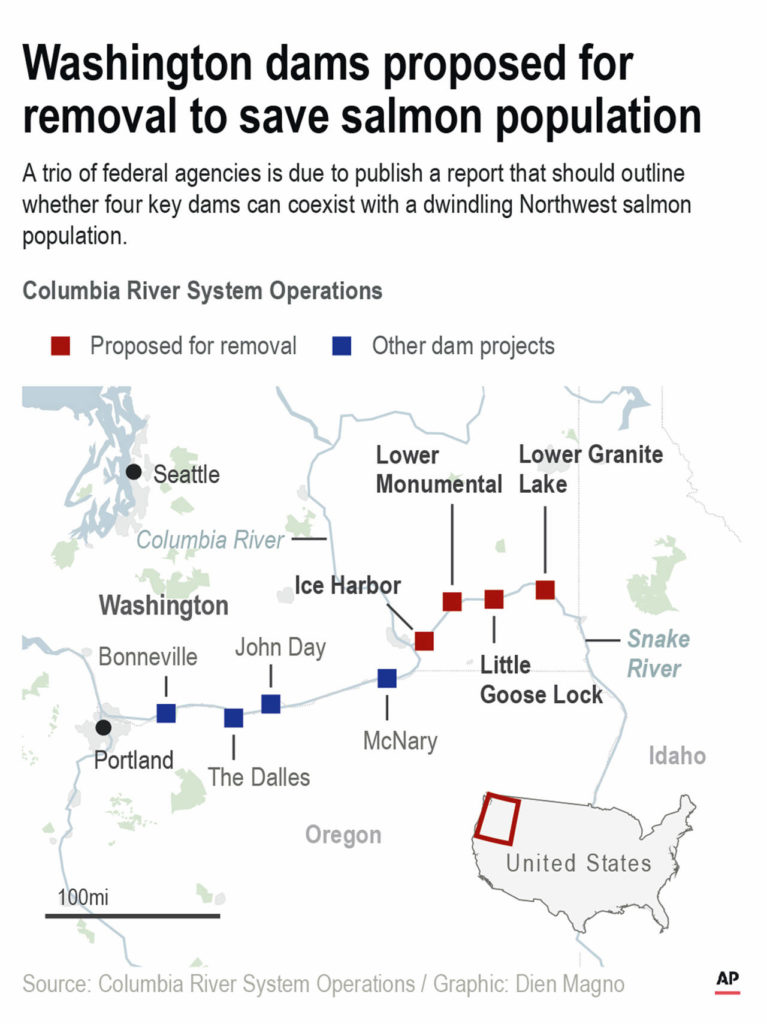
A long-awaited federal report out Friday rejected the idea of removing four hydroelectric dams on a major Pacific Northwest river in a last-ditch effort tosave threatened and endangered salmon, saying such a dramatic approach would destabilize the power grid, increase overall greenhouse emissions and more than double the risk of regional power outages.
The four dams on the lower Snake River are part of a vast and complex hydroelectric power system operated by the federal government in Washington, Oregon, Idaho and Montana. The massive dams, built in eastern Washington between 1961 and 1975, are at the center of a years-long battle that pits the fate of two iconic Pacific Northwest species — the salmon and the killer whale — against the need for plentiful, carbon-free power for the booming region.
Environmental groups that have pushed for years for the dams to come down immediately blasted the report. The three agencies in charge of overseeing the sprawling hydropower system recommended an alternative that doubles down on an approach that includes spilling more water over the dams when juvenile salmon are migrating — a tactic already being used.
“Rather than seizing this opportunity to heed the public’s call for working together for a solution that revives salmon populations, the draft plan is built on the same failed approach the courts have rejected time and again,” said Todd True, an attorney for Earthjustice who has represented environmentalists and fishing groups in ongoing litigation over the dams.
Dam removal opponents, however, said the report presented a balanced solution that won’t burden ratepayers or disrupt the region’s power supply.
“Once again, the science has determined that destroying the four Lower Snake River dams would have high environmental and economic costs,” said Todd Myers, environmental director at the Washington Policy Center, a conservative think tank.
The 14 federal dams on the Columbia and Snake rivers together produce 40% of the region’s power — enough electricity to power nearly 5 million homes, or eight cities roughly the size of Seattle. Among the entities that rely on that power is the Snohomish County Public Utility District.
The dams also have a system of locks that allows cities nearly 500 miles inland access to Asian markets via barges that float down the rivers to the Pacific Ocean. Roughly 50 million to 60 million tons of cargo navigate the Snake and Columbia river system annually.
Yet the towering dams have proven disastrous for salmon that struggle to navigate past them on their way to and from the Pacific Ocean. Salmon are unique in that they hatch in freshwater streams, then make their way hundreds of miles to the ocean, where they spend years before finding their way back to mate, lay eggs and die.
Snake River sockeye were the first species in the Columbia River Basin listed under the Endangered Species Act in 1991. Now, 13 salmon runs are listed as federally endangered or threatened. Four of those runs return to the Snake River.
The Columbia River system dams cut off more than half of salmon spawning and rearing habitat, and many wild salmon runs in the region have 2% or less of their historic populations, said Meg Townsend, an attorney for the Center for Biological Diversity.
On the way to the ocean, juvenile salmon can get chewed up in the dams’ turbines, she said. The adults returning from the ocean must navigate fish ladders — concrete chutes that bypass the dams — but they can become bottle-necked before reaching them and get picked off by predators, Townsend said.
Until recently, young salmon were sent by truck or barge around the dams or passed through the turbines or bypasses. An interim agreement that took effect last year prioritized the “flex spill” strategy of increasing the water in spillways to send more fish over the tops of the structures. This approach allows the U.S. government to adjust the spill level according to power demands.
The effect on the long-term survival of juvenile salmon won’t be known for several years, when biologists can start counting the adult fish that return from the ocean.
Scientists also warn that southern resident orcas are starving to death because of a dearth of the chinook salmon that are their primary food source.
The Pacific Northwest population of orcas — also called killer whales — was placed on the endangered species list in 2005. A mother orca that carried her dead baby on her back for 17 days brought international attention in 2018 as their numbers have dwindled to 72 animals.
Opponents of dam removal say they want salmon to flourish, but they aren’t sure breaching four major hydroelectric dams will help — and it could instead damage the regional economy and the stability of the power supply.
Reservoirs behind some of the dams allow the Bonneville Power Administration to even out the more erratic power supply from wind and solar by spilling water to generate electricity on short notice. And a move away from low-cost coal plants in the Pacific Northwest has some worried about what the future could hold for ratepayers if the Snake River dams are removed, said Kurt Miller, of Northwest River Partners, which represents community-owned utilities across Oregon, Washington, Idaho and Montana.
“If worldwide salmon populations are doing poorly because of climate change and carbon, does it make sense to tear out 1,000 average megawatts of carbon-free electricity?” he said. “For so many reasons, it’s bad public policy.”
The report addressed those concerns, noting hydropower generation would decrease by 1,100 average megawatts under average water conditions, and 730 average megawatts under low water conditions. The risk of a regional power shortages would more than double and the lowest-cost replacement power would be $200 million a year, it said. Those adjustments would increase the wholesale power rate up to 9.6%, the authors wrote.
U.S. District Judge Michael Simon ordered the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, the Bureau of Reclamation and the Bonneville Power Administration to revisit the impact of the hydroelectric system in 2016 while overseeing litigation over salmon.
In all, three federal judges have thrown out five plans for the system over the decades after finding they didn’t do enough to protect salmon.
Friday’s report is a draft and will be subject to 45 days of public comment. The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration will next analyze the proposal to determine if it does enough to protect salmon and orcas — a process that should be completed by June.
A final report is expected in September.
Talk to us
> Give us your news tips.
> Send us a letter to the editor.
> More Herald contact information.