Governor pitches budget plan with $2.5B in new spending
Published 11:20 am Thursday, December 14, 2023


By Jerry Cornfield / Washington State Standard
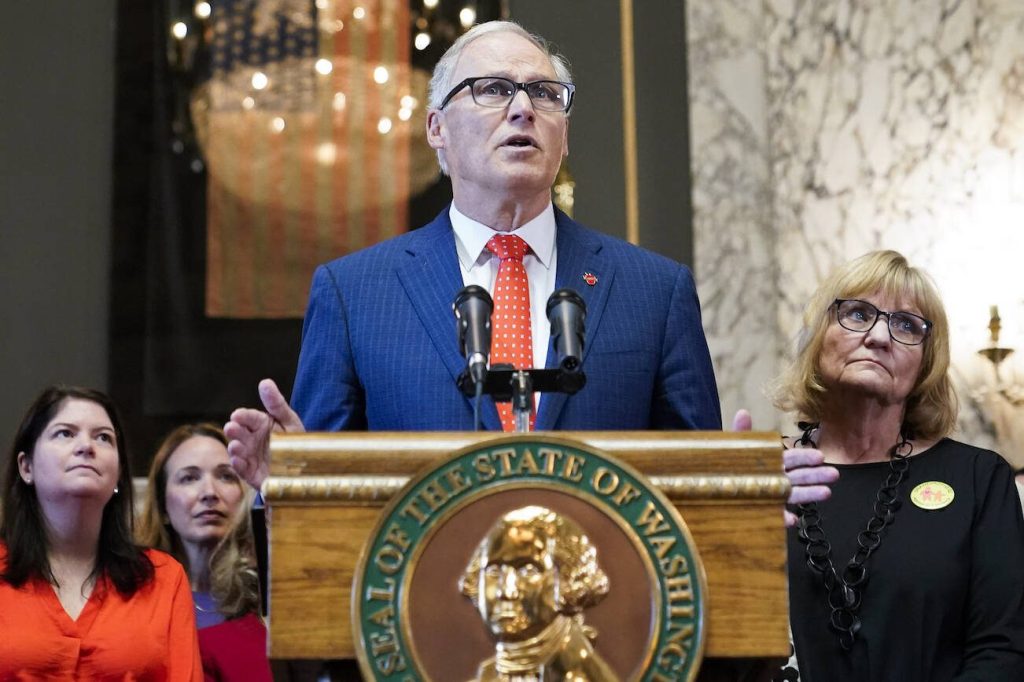
Washington Gov. Jay Inslee on Wednesday outlined a plan to boost state spending by nearly $2.5 billion in the next 18 months with the largest sums devoted to increasing behavioral health services, reducing homelessness, and combating climate change.
His proposal relies on higher-than-expected tax collections and robust proceeds from the sale of pollution allowances. It would supplement spending in the operating, capital and transportation budgets adopted by the Legislature earlier this year. Washington runs on two-year budget cycles with the current one ending June 30, 2025.
The three-term Democratic governor wants to pour another $1 billion into programs in the $69.8 billion operating budget. No new taxes are proposed.
Nearly half the increase, $448.7 million, is earmarked for increasing capacity in the state’s behavioral health system through the hiring of staff and addition of treatment beds for youth and adults. Another $140 million is sought for addressing homelessness and expanding housing and $64 million is to deal with the deadly spread of fentanyl, a powerful opioid Inslee called the “nuclear weapon of drugs.”
“This is a budget that is changing lives. There are some numbers attached to it but these numbers aren’t important,” he said at an afternoon news conference. “What’s important are the lives.”
Into the weeds
This is Inslee’s last supplemental budget before he leaves office. The spending priorities reflect the major challenges he’s encountered since taking office in 2013.
He had to ramp up spending on behavioral health, largely in response to the Trueblood case in which a federal court found the state’s long wait times for mental health treatment and evaluations violated the constitutional rights of people in jail waiting for those services before they can be deemed competent to stand trial.
“This will not be the end of our effort,” he said Wednesday. “What we have done is to do everything we can as fast as we can.”
To help those without shelter, Inslee is seeking $100 million for the state’s Rapid Capital Housing Acquisition fund, which pays for emergency housing like tiny home villages, $10 million for the Department of Transportation to continue clearing encampments on state properties and $30 million for other programs, like rent assistance and expanding legal aid for tenants facing eviction. There’s also money for mental health and substance use disorder services for people who are unhoused or transitioning out of homelessness.
Inslee was pressed Wednesday on the expense of housing and homelessness-related programs as more than $100 million has been spent and roughly 1,000 people assisted.
They are expensive and necessary investments, he said. In the long-term, the state gets housing facilities that are “permanent assets” and will serve many people for years to come, he added.
Inslee is seeking $64 million for programs serving individuals and families affected by illegal opioids on top of the roughly $200 million included in the current two-year state budget.
On education, he is proposing to drive more dollars to school districts to pay for special education by increasing the funding cap. He estimates this will make $17 million more available to districts with large numbers of students with special needs.
Also in education, Inslee is requesting $64 million to cover a $3 an hour raise for 32,000 paraeducators whom he described as “some of the most important people in our education system.”
Capital gains and climate
Washington’s new capital gains tax brought in $890 million in its first year, giving Inslee an unexpected chance to provide smaller school districts with much-needed dollars for construction and renovation projects.
By law, the first $500 million from the tax each year is deposited in the Education Legacy Trust Account, a source of dollars for public schools, early childhood education and child care. Anything above that amount goes into the common school construction account, which is part of the capital budget. Some of that excess was not spent so it can be used in a future budget cycle.
Inslee made few moves with the transportation budget, offering no suggestions on how the state should deal with soaring costs to build new ferries and freeways and remove salmon-blocking culverts. He said he was “largely following” the desires of House and Senate leaders.
On climate, Inslee’s plan contains $900 million in new expenditures using funds generated through the cap-and-trade program. Of the total, $150 million will be used to provide a one-time $200 credit on residential electricity bills for an estimated 750,000 low- and moderate-income Washington families.
Sen. Lynda Wilson, R-Vancouver, the lead budget writer for Senate Republicans, seized on the voucher as evidence that the Climate Commitment Act is causing economic pain.
“This new voucher proposal is a tacit acknowledgment of the burden the governor’s misguided and misleading policies have placed on the people of Washington,” Wilson said in a statement. “Yet this proposal provides only one-time relief, and for only a small segment of the population. We deserve better.”
Inslee’s budget is the first of three budget proposals the public will see in the weeks ahead.
The Democratic-controlled House and Senate will each present their own supplemental spending plans during the 60-day legislative session that begins Jan. 8.
Washington State Standard is part of States Newsroom, a nonprofit news network supported by grants and a coalition of donors as a 501c(3) public charity. Washington State Standard maintains editorial independence. Contact Editor Bill Lucia for questions: info@washingtonstatestandard.com. Follow Washington State Standard on Facebook and Twitter.