By Lara Williams / Bloomberg Opinion
I dearly hope to have children of my own some day. What they do with their time on Earth is theirs to choose, but the type of world they’ll inhabit will be determined by me and all of us — now — while they’re still a figment of my imagination. It’s a simple concept, but that doesn’t keep it from becoming increasingly dire.
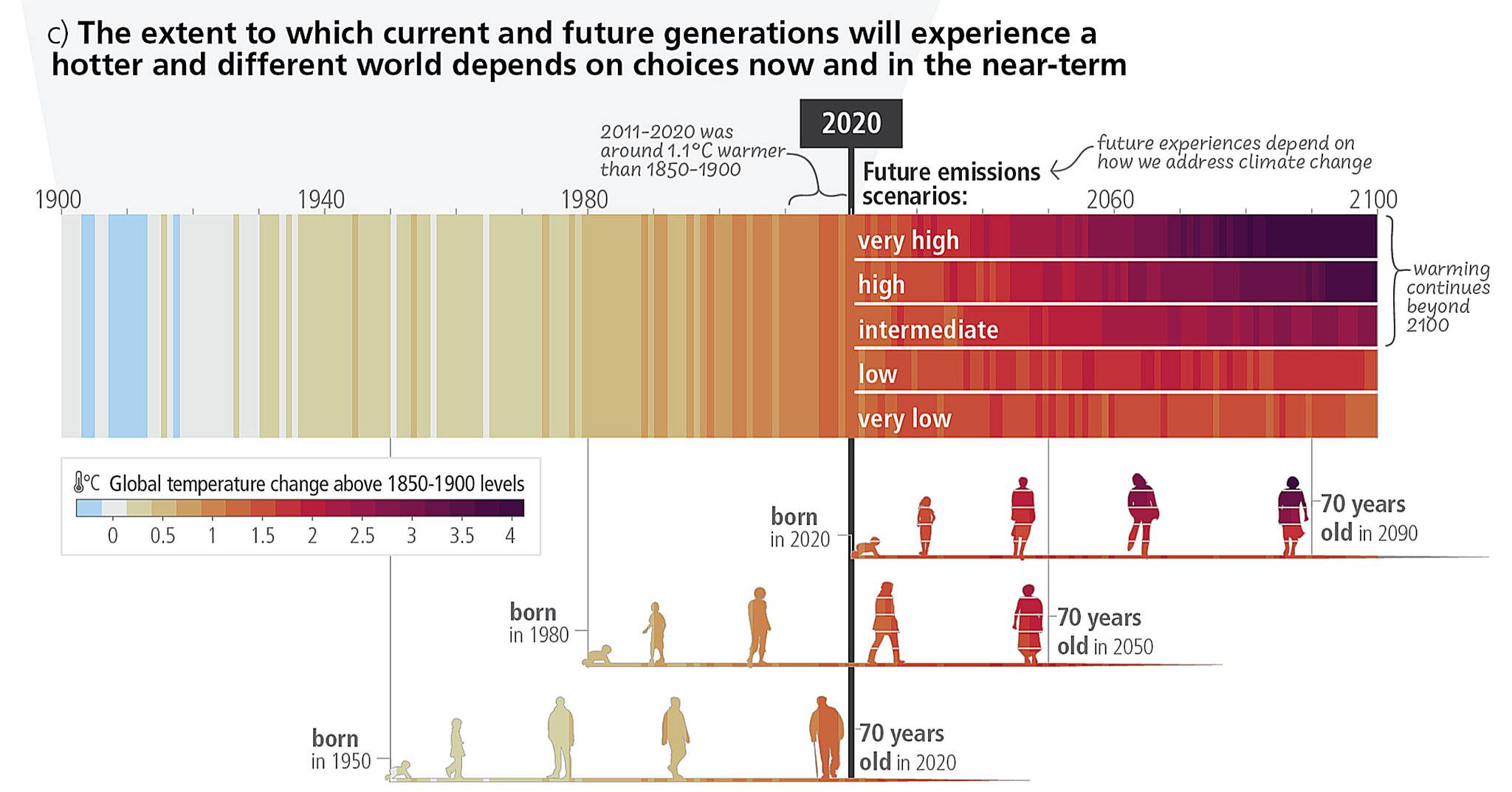
That seriousness was brought home to me by a graphic in the latest UN Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) Synthesis Report. The illustration is one of the first in the document; an update of the warming stripes first concocted by Ed Hawkins, professor of climate science at the University of Reading in England.
The color bars are dramatic, moving from cool blue to deep purple; they portray the changes in global temperature since 1900. The newly tweaked version in the IPCC report version projects several scenarios out to the year 2100 based on what we might do about our global emissions.
The revision that’s stuck in my head is the illustration with human silhouettes at the bottom of the graphic, courtesy of IPCC graphic officer Arlene Birt: It shows the lifespans of people born in 1950, 1980 and 2020 color-coded to their chronological place in the warming of the planet. Each generation has a completely different relationship to the Earth’s crisis.
“The warming I have experienced up to present day is much larger than the warming my parents experienced up to the same age,” says Alex Ruane, a member of the IPCC core writing team and co-director of the climate impacts group at the NASA Goddard Institute for Space Studies. “And when you look at the same sequence of icons for the present-day generations, you can see that the warming is much steeper.”
It also reveals just how much that the decisions made today will have huge effects on the world of tomorrow. By the time a baby born in 2020 becomes a septuagenarian, the difference in the potential temperature change is larger even than the warming we have experienced up to the present day. In a scenario in which our emissions remain high, a 70-year-old in 2090 could be living on a planet that’s 4 degrees Celsius warmer than pre-industrial levels. If we’re successful in making deep, rapid and sustained cuts to our emissions, the planet will be only about 1.5C warmer. That’s a difference of 2.5C. The planet is currently 1.1C hotter than the average between 1850 and 1900; and that surge has already had substantial impacts on water availability, heat, and the health of both humans and animals.
The IPCC doesn’t just highlight intergenerational climate injustice. It also focuses on injustice and the unequal suffering inflicted by global warming. Between 2010 and 2020, human mortality from floods, droughts and storms was 15 times higher in highly vulnerable regions; typically developing countries without access to technology and other measures to mitigate and adapt to the rising temperatures. Global heating’s adverse impacts will continue to disproportionately affect these populations. The unjust thing? They’ve barely contributed to the climate crisis but are bearing the consequences.
Unless policies are more effective, the IPCC suggests we’re on track for 3.2C of warming by 2100. It’s hard to say exactly what that world will look like. What we do know at this point doesn’t sound good. One study suggests an increase in the chances of major heatwave across the world. It was around 5 percent between 1981 and 2010. If we get to 3C by the turn of the next century, it will be 80 percent. Cities such as Amsterdam and Bangkok would likely disappear beneath rising seas, alongside practically all of the Maldives and the Seychelles. Billions of people in the most exposed areas would become climate refugees.
Ruane is keen to emphasize that we still have agency here. The future doesn’t have to look like that at all. But avoiding the nightmare scenarios will greatly depend on what we do in the next decade.
Dr. Hoesung Lee, chair of the IPCC, said in a press conference that the report’s overall message was one of hope. There are feasible, effective and low-cost tools available to us right now that would enable us to meet the Paris goal of a 1.5C increase. But to do that, we’ll have to slash emissions by 50 percent by 2030. It’s technically possible, but it won’t be easy.
However, it’s hard to keep hope alive when governments — including ones who claim they are committed to slashing emissions to net zero — are still approving new fossil fuel projects. According to the IPCC, existing carbon-heavy infrastructure already exceeds the remaining carbon budget for limiting warming to 1.5C.
Projects such as ConocoPhillips’s Willow oil drilling project in Alaska and the newly approved coal mine in the United Kingdom are baffling — perhaps even criminal — in the face of all that we know about the harm they would inflict on generations yet to be born. Indeed, two lawsuits have already been filed against the Willow project — alleging the Biden administration broke federal law to approve it — and many expect to see a wave of stakeholders — especially children and marginalized groups — use the courts against governments and companies to fight for their future.
Governments, banks and fossil fuel companies aren’t ready for these lawsuits. So here’s a suggestion to help them avoid litigation: Put an end to funding and subsidies for such projects and redirect the money toward climate action, paying special attention to places that currently lack the resources to decarbonize.
That is a no-brainer. And the bounty is immense. The IPCC report cites dozens of co-benefits including improved human health, increased agricultural productivity, gains in innovation and costs savings from avoiding the worst climate-related damage and catastrophes.
At the press conference, climate scientist Peter Thorne referenced the late author Douglas Adams, saying: “We are beyond the point that climate change can be ‘somebody else’s problem.’”
It’s our problem, and it’s time we start acting like the lives of our children are at stake. They are.
Lara Williams is a Bloomberg Opinion columnist covering climate change.
Talk to us
> Give us your news tips.
> Send us a letter to the editor.
> More Herald contact information.