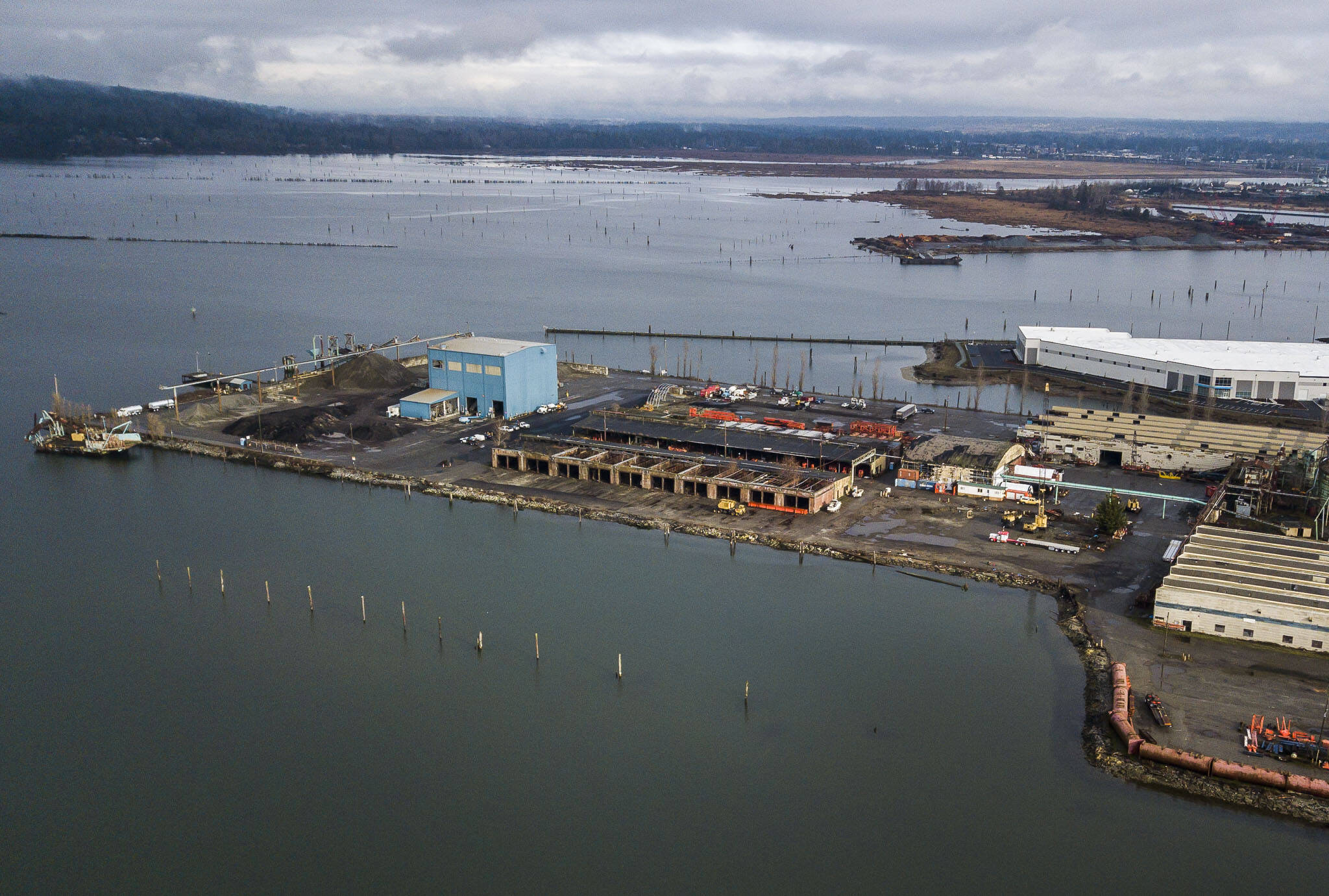
EVERETT — The Port of Everett voted earlier this month to accept a donation of private land adjacent to the contaminated former Jeld-Wen site — a donation port managers say will ensure environmental fallout from the site is properly managed when cleanup efforts begin, possibly by the end of 2023.
The 9.6 acres of bayside, mostly submerged land, referred to in port documents as Wicks Tide Flats, sit just north of the former Jeld-Wen property at 300 West Marine View Drive. The Oregon-based door manufacturer operated out of the Port Gardner plant since purchasing the former E.A. Nord Co. in 1986. The Everett location closed in 2005.
Along with several other portside industrial sites, the former Jeld-Wen plant has been flagged for environmental cleanup since at least the mid-2000s. State Department of Ecology investigations turned up soil and groundwater contamination dating back to the site’s use as a wood treatment plant in the 1940s, including creosote, dioxin, lead and mercury. Studies also found PCBs, highly carcinogenic compounds banned in the U.S. since 1979, in the groundwater and sediment.
The tide flats near the plant were privately owned by Wick Family Properties, LLC, and were likely historically used for log rafting and storage for the mills that once lined the waterfront. According to port documents, a representative approached the port in late 2022 requesting to donate the land, valued at $192,600, in exchange for “environmental indemnification” for the owners.
The port is responsible for taxes and fees associated with the donation, estimated at a maximum of $15,000. Board members voted to accept the donation at their meeting Jan. 10.
Port spokesperson Catherine Soper said the donated tide flats were “a natural extension” of the port’s existing land holdings in the area, including the contaminated former Bay Wood sawmill site nearby. The port began cleanup efforts at Bay Wood in 2020 with the intent of developing the site into a new manufacturing hub.
“Our interest in acquiring this land, ultimately, is that we’re a port and it’s waterfront property,” Soper said. “We know how to manage tidelands because we already own 100-plus acres of them, and we have plenty of experience in cleanup. The benefits of the cost greatly outweigh the small fee that we have for closing costs here.”
Soper said the opportunity for the port to acquire the land came “out of the blue,” so managers don’t yet have plans for the site’s post-cleanup use. She said one possible outcome would be using the site as a dumping ground for sediment dredged from the Snohomish River during routine maintenance to keep the river navigable by ships.
Since any contamination on the donated land is likely to have come from the upland Jeld-Wen site, cleanup efforts will likely be covered under the company’s existing commitments, Soper said. A 2008 agreed order between Jeld-Wen and the Department of Ecology places much of the responsibility for carrying out the cleanup on the company.
Under standard agency practice, all current and former owners of a contaminated site are considered potentially liable parties. A Jan. 18 letter from the Department of Ecology notified the former owners that despite Wick Family Properties claiming it was not responsible for the release of hazardous substances at the site, the agency had found “credible evidence” to indicate they were potentially liable. The former owners’ financial responsibility will be determined as the project advances, the letter said.
Mahbub Alam, an engineer with the state Department of Ecology who has been working on the Jeld-Wen site for six years, said the port’s acquisition of the neighboring tidelands is not likely to change the agency’s cleanup efforts. Any settlement of indemnification or financial responsibility is determined among Jeld-Wen, the port and the former owners, and it doesn’t impact the department’s ultimate goal of remediation, Alam said.
Ecologists finished an initial investigation and feasibility study on the site in December 2021. Alam said the next step is creating a draft action plan detailing the cleanup process. The department will hold a public comment period on the plan before it is finalized.
Much of the most highly contaminated soil from the site will likely be removed and backfilled, he said, but in some places offshore, contaminants may extend as far as 10 feet into the ground. Removing it all could cause slope instability, among other issues, so in those cases remaining contaminants will be contained by capping with a barrier designed to withstand water erosion.
Alam said the project’s timeline depends heavily on negotiations between the department and other involved parties. Under the most “aggressive” scenario, he said removal work could begin in late 2023 or 2024.
Riley Haun: 425-339-3192; riley.haun@heraldnet.com; Twitter: @RHaunID.
Talk to us
> Give us your news tips.
> Send us a letter to the editor.
> More Herald contact information.